资讯详情
近日,我协会郝际平会长等人合著的学术论文(Buckling of stepped columns considering the interaction effect among columns)(《顾及柱间相互作用效应的阶梯柱屈曲》,在《Journal of Construction Steel Research》杂志发表(论文编号为177106416),被国际著名科技机构“工程进展”(Advances in Engineering, AIE)遴选为关键科学文章,并进行了重点报道,类别为土木工程。另外两位作者分别为中国西安建筑科技大学土木工程学院助理教授田炜峰博士、钟炜辉教授。

AIE是一个成立于2005年的加拿大组织,该组织的成立旨在及时快速地将能够为人类造福的工程领域重要的科学研究成果和创新技术在世界各地迅速传播,其主要的读者和受众是受过良好教育的工程和物理界的科学家、教授和学生。
AIE推广论文是经过国际专家顾问组高度筛选后确定的,AIE每周会在全球范围内工程领域发表文献中选出最多20篇的优秀论文进行特别报道,被选中发布推广的论文中选率少于千分之一,方向包括通用工程(航空航天、通讯、计算机、农业、工业)、化学、电子、机械、土木、纳米技术、材料、应用物理、生物医学工程。被AIE推广的论文需要具有特殊的科学重要性并能够被广大的科学读者所理解。AIE每月的阅读量高达65万次,其读者群35%为北美,33%为欧洲,30%来自亚洲。AIE除受到全球主要研究机构的关注外,也被全球排名前50位的工程公司所链接,用于跟踪突破性科技进展。
AIE专题报道中介绍郝际平:是中国西安建筑科技大学土木工程学院的教授,研究钢结构、竹结构和创新结构系统。他在多个与土木工程相关的国家委员会任职,是中国建筑金属结构协会主席。
田为峰博士研究重点是钢结构的稳定性和创新的抗震荷载系统,他目前的大部分研究是关于阶梯钢筋的屈曲和钢板剪力墙的后屈曲行为。钟炜辉博士的研究重点是钢结构的稳定性和钢结构的连续倒塌,特别是钢框架的抗连续倒塌性能。
(以下从AIE“土木工程”专题报道中翻译)
顾及柱间相互作用效应的阶梯柱屈曲
意义:
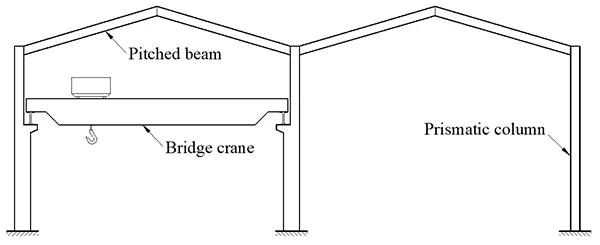
厂房中使用的框架需要足够坚固,以承受高起重机荷载。通常,此类框架由阶梯柱制成,阶梯柱具有较轻的上段和较宽的法兰横截面下段,以适应起重机荷载。然而,与棱形柱不同,阶梯柱由于非均匀横截面的影响和轴向(起重机)荷载的存在,表现出显著不同的屈曲行为。为此,阶梯形柱的屈曲行为引起了广泛的研究关注。自20世纪70年代Timoshenko的开创性工作以来,已经开展了大量的理论和实验研究,以计算不同柱的屈曲荷载,确定其有效长度系数和力学行为。这些研究令人满意地解决了与屈曲行为相关的各种问题,并已扩展到多步骤和非均匀柱。根据之前的研究,已制定并采用了阶梯柱的设计方案。
尽管取得了进展,但大多数现有研究集中于单个柱的行为,而忽略了不同柱之间相互作用的影响,导致框架设计不准确。为了应对这一挑战,开发了两种手动设计方法,以确定阶梯柱设计中使用的有效长度系数和屈曲荷载。然而,现有的方法不适用于某些设计方案,如斜屋顶门式刚架和多开间框架,因为它们忽略了屋顶的倾斜角度和柱之间的相互作用效应。因此,开发一种适用于所有设计场景的设计方法是非常可取的。
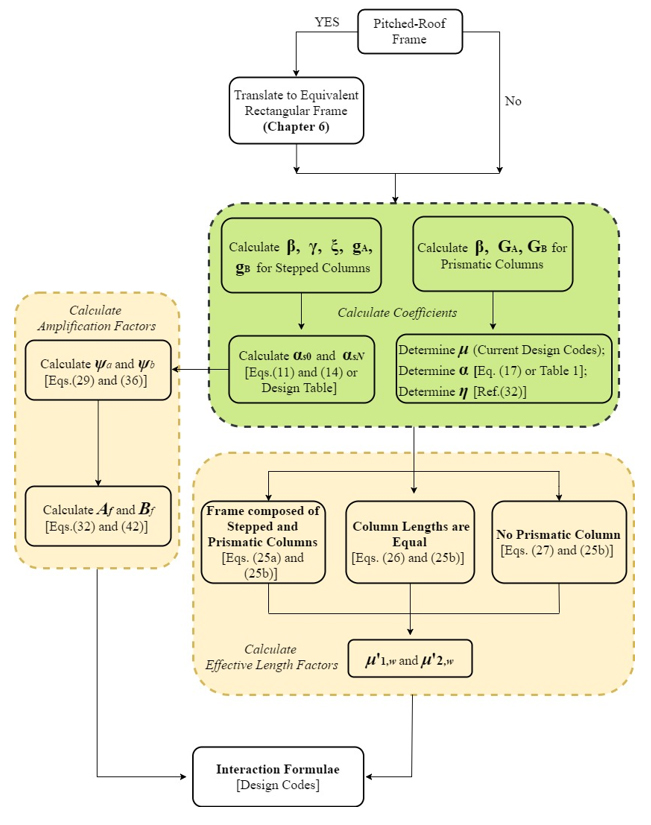
虽然计算机软件和有限元建模非常流行,但手工计算方法是必不可少的,因为它们可以更好地理解柱的设计过程和力学运转状态。为此,西安建筑科技大学的田炜峰博士、郝际平教授、钟炜辉教授提出了一种简便、准确的计算阶梯柱框架二阶效应和有效长度因子的手工计算方法。该方法考虑了不同阶梯柱之间的相互作用效应。这项工作目前发表在《Journal of Construction Steel Research》(《建筑钢研究杂志》)上。
该方法基于负刚度的概念,适用于不同的框架类型。该概念用于计算有效长度系数,该系数考虑了不同阶梯柱之间的相互作用效应。接下来,对二阶效应进行了理论分析,得出了确定弯矩放大系数和挠度系数的表达式。作者还提出了一种考虑阶跃柱屋角影响的实用方法。最后,通过非线性静力分析和特征值分析,验证了该方法的实用性。
结果表明,与现有方法相比,该方法在获取不同柱的相互作用效应和提供有效长度因子的准确估计方面具有优势。在位移和弯矩差异分别为0.6%和3.4%的情况下,对二阶效应进行了令人满意的估计。弯矩的微小误差归因于柱变形曲线的简化。此外,所提出的方法准确地考虑了屋顶角度的影响,适用于各种框架类型。
综上所述,本研究发布了一种简单可行的方法,用于计算有效长度系数,并通过考虑多个柱的相互作用效应来评估阶梯柱的屈曲性能。该方法使作者能够使用与侧向荷载系数相对应的刚度系数值,以确保用于计算有效长度系数的表达式和方程的物理意义。结果证明了该方法的有效性和实用性。作者进一步提出了改进现行设计规范的建议。在一份关于工程进展的声明中,作者表示,他们的研究结果和建议将使工程师和制造商能够为工厂建筑中的阶梯柱开发成本效益高、可靠的设计。
所提方法的实施流程图:
(Flowchart for implementing the proposed method)
阶梯柱框架:
(Frame with stepped columns)
附专题报道中英文原文
Buckling of stepped columns considering the interaction effects amongst columns
Significance
The frames used in mill buildings need to be robust enough to withstand the high crane loads. Usually, such frames are made of stepped columns with a lighter upper segment and a heavy wide-flange cross-section lower segment to accommodate the crane load. However, unlike prismatic columns, stepped columns exhibit considerably varying buckling behavior due to the effects of the non-uniform cross-section and the presence of axial (crane) load. To this end, the buckling behavior of stepped columns has drawn significant research attention. Since Timoshenko’s pioneering works in the 1970s, numerous theoretical and experimental studies have been carried out to calculate the buckling loads of different columns, establish their effective length factors and mechanical behaviors. These studies have satisfactorily addressed various problems associated with buckling behaviors and have been extended to multi-step and non-uniform columns. Following the previous studies, design protocols for stepped columns have been established and adopted.
Despite the progress, most existing studies concentrate on the behaviors of individual columns while neglecting the effects of the interaction amongst different columns, leading to inaccurate frame design. In an effort to address this challenge, a couple of hand manual hand-design methods have been developed to determine the effective length factors as well as buckling loads used in the design of stepped columns. Unfortunately, the existing methods are not suitable for some design scenarios, such as pitched-roof portal frames and multi-bay frames, since they ignore the inclination angles of the roof and interaction effects amongst columns. Therefore, developing a design method applicable to all design scenarios is highly desirable.
Although computer software and finite element modeling are quite popular, hand calculation methods are indispensable because they better comprehend the design process and mechanical behaviors of the columns. Therefore, Dr. Weifeng Tian, Professor Jiping Hao, Professor Weihui Zhong from Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology proposed a simple and accurate hand calculation method for evaluating the second-order effects and effective length factors on stepped column-based frames. This method accounts for the interaction effects amongst different stepped columns. The work is currently published in the Journal of Construction Steel Research.
The proposed method was based on the concept of negative stiffness that is applicable to different frame types. This concept was used to calculate effective length factors accounting for the interaction effects amongst different stepped columns. Next, the second-order effects were theoretically analyzed to develop expressions to determine the moment amplification and deflection factors. The authors also presented a practical method considering the influence of roof angles with stepped columns. Lastly, the practicability of the proposed method was validated through nonlinear static and eigenvalue analysis.
Results demonstrated the superiority of the proposed method in capturing the interaction effects of different columns and providing accurate estimates of effective length factors than the existing methods. A satisfactory estimation of the second-order effects with 0.6% and 3.4% differences in displacement and bending moment, respectively, was achieved. The slight inaccuracy of the bending moment was attributed to the simplification of the column deformation curve. In addition, the proposed method accurately accounted for the influence of roof angle, and it applies to a wide range of frame types
In summary, a simple and feasible approach for calculating effective length factors and evaluating the buckling behavior of stepped columns by considering the interaction effects of multiple columns were reported. The method enabled the authors to use stiffness factor values corresponding to lateral load coefficient to ensure the physical significance of the expressions and equations used to calculate the effective length factors. The results demonstrated the validity and practicability of the proposed approach. The authors further provided recommendations for improving the current design codes. In a statement to Advances in Engineering, authors said their study findings and the recommendations will enable engineers and fabricators to develop cost-effective and reliable designs for stepped columns in mill buildings.
Reference
Tian, W., Hao, J., & Zhong, W. (2021). Buckling of stepped columns considering the interaction effect among columns. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 177, 106416.
来源:《中国建筑金属结构》杂志社
